Health Disparities Program
The Health Disparities Team works across DPH to ensures the inclusion of measurable equity goals for clinical services to develop or modify programs in addressing health disparities.
Community: Neighborhood Engagement Sessions

Background:
•Originated from the vision of the former Director of the Office of Health Equity, Dr. Ayanna Bennett and based on input from leaders in community-based organizations.
Purpose:
•Provide a space to amplify community voices, bridge gaps, and build pathways for DPH and community collaboration.
•Specific examples include: helped Public Health Infrastructure grant team strengthen knowledge and understanding of social determinants of health in priority neighborhoods and build relationships with CBO's.
Accomplishments and Findings:
•The OHE Health Disparities Program has organized 7 walking sessions in the following priority neighborhoods: Bayview Hunters Point, Mission, Chinatown, Potrero Hill, Excelsior, Visitacion Valley, and BVHP - Shipyard with the participation of 22 CBOs.
•109 members from the SF Health Network, Population Health Division, Primary Care, and DPH executive leadership participated in sessions.
•7% of DPH participants surveyed live in the neighborhood where they work.
•A majority of the participants (72%) reported that they better understood the needs of the neighborhood in which they primarily work after the tour.
•Walking sessions will transition to DPH- Primary Care to continue with assistance from the OHE Health Disparities Program.
“Thank you so much for this opportunity! It was by far one of the most insightful experiences I've had at DPH.” (Participant)

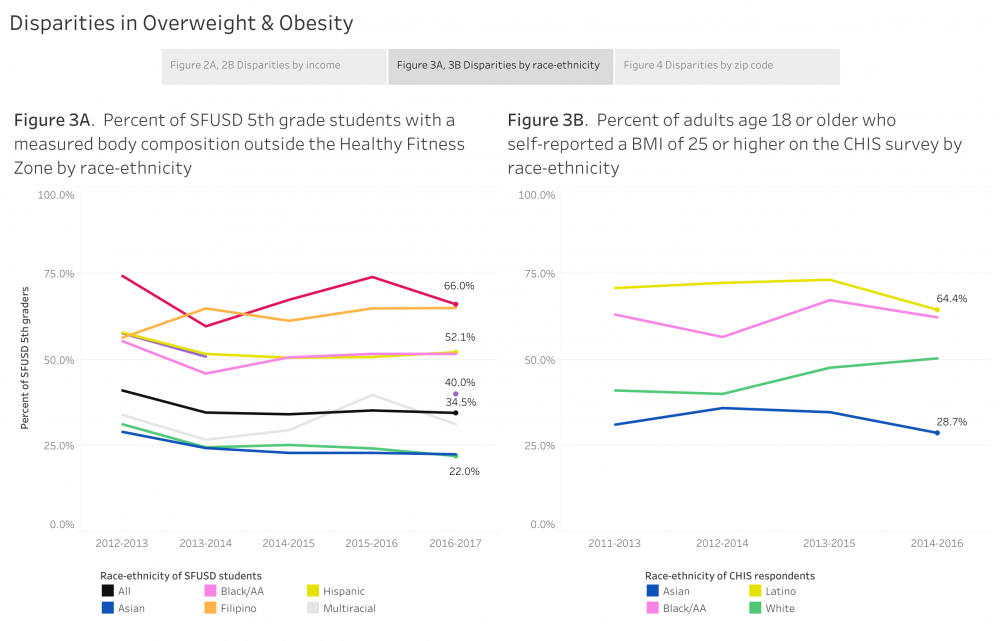
Adult & 5th Grade Obesity
- Over 30 percent of 5th grade SFUSD students and over 40 percent of adults in San Francisco are overweight or obese
- Overweight or obesity disproportionately affects individuals with low-income and individuals of color
- For individuals with low income, increased risk of becoming overweight or obese is associated with specific zip codes and community-level factors, such as type of housing, child care center, and hospital
All-Cause Mortality
- The Leading causes of death are predominately chronic diseases including heart diseases, cancers, Alzheimer’s, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, and Diabetes.
- Mortality rates of both Alzheimer’s Disease and Diabetes are increasing in San Francisco.
- Additional important causes of premature death in San Francisco include assault, traffic accidents, injuries and HIV. While each of these kill relatively few residents, those afflicted are typically younger.
- Overall Life Expectancy is high in San Francisco with the typical resident living to 83 years. Similar to trends seen nationwide, Life Expectancy in San Francisco has decreased since 2014.
- Life expectancy varies by race/ethnicity and gender. Black/African Americans and Pacific Islanders have the lowest life expectancy.

COVID Vaccination Rates
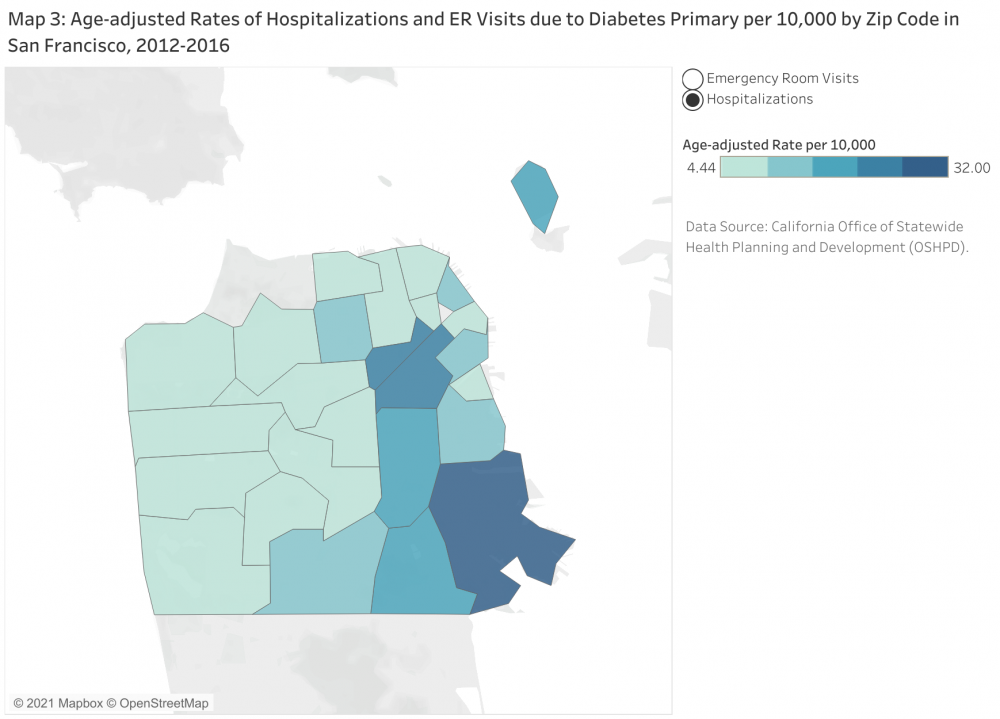
Diabetes Admission
- Over the past 30 years the prevalence of diabetes among Black/African Americans quadrupled.
- Black/African Americans are 70 percent more likely to develop diabetes than Whites.
- In San Francisco, rates of hospitalization are 3-6 times higher and rates of death are 2-3 times higher among African Americans compared to all other race/ethnicities.
- Residents in the eastern zip codes (94102, 94110, 94115, 94124, and 94130) are more likely to be hospitalized due to diabetes than those living elsewhere in San Francisco.

Heart Disease Admission
- The hospitalization rates due to hypertension or heart failure for Black/African Americans are 3-5 times higher than all other races.
- Hospitalization and emergency room visit rates due to cardiovascular disease are higher among residents in the southeast half of San Francisco.


HIV
- The estimated rate of new HIV infection in San Francisco has decreased from 56 per 100,000 in 2012 to 40 per 100,000 in 2014.
- Incidence rates for HIV and each STD are higher among men


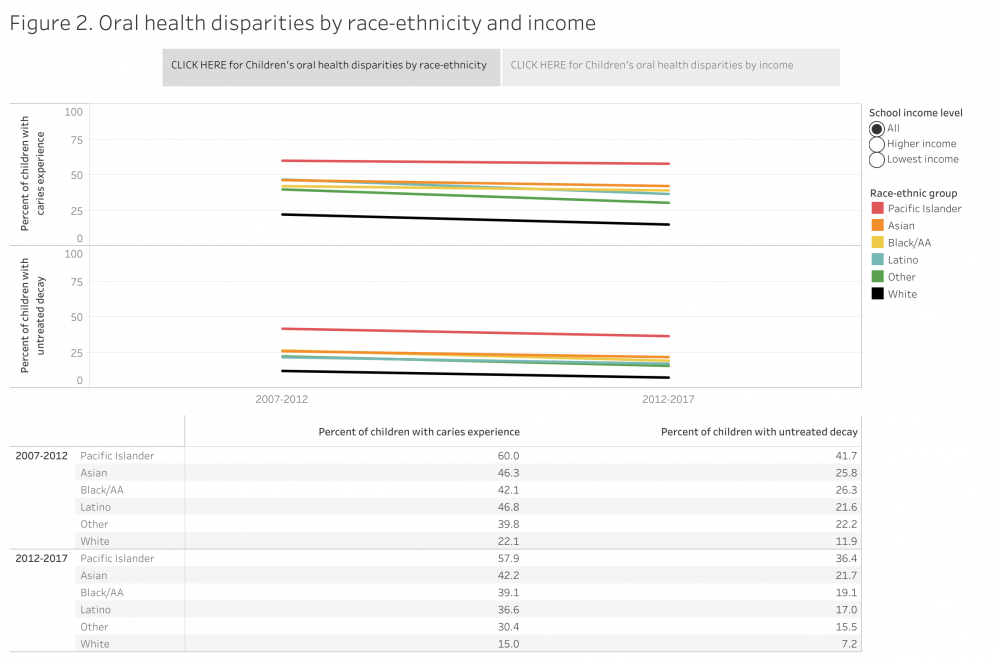
Kindergarteners Who Have Untreated Caries
- Low-income, Asian, Black/African American, and Latino children are twice as likely to experience tooth decay by the time they are in kindergarten than higher-income and White children
- One third of students in San Francisco public schools have experienced tooth decay by the time they are in kindergarten
- Dental services to prevent tooth decay reach fewer than 20 percent of Denti-Cal eligible children ages 1-2 years in San Francisco
Smoking
- In 2015-2016, 10.85% of adults in San Francisco reported they were current cigarette smokers, which slightly increased from 8.76% in 2013-2014; but the percentage was lower than California (12.40%).
- Men are almost 3x more likely to smoke cigarette than women and the percentage among residents who lived below 200% of Federal Poverty Level is 2x higher than residents who lived above 200% of Federal Poverty Level.
- Similar to adults, male student are more likely to smoke cigarettes than female students. The percentage was higher among White and Black students and it also increases along with age.
- In 2016, 0.98% of new mothers in San Francisco reported smoking before or during pregnancy. The percentage has been dropping in the last 10 years from 2.71% in 2007. However, it was still 6-15 times higher among Black/African American women (6.83%) than all other races and ethnicities.
- Districts in San Francisco with higher concentrations of smokers, ethnic minorities, and youths are associated with a higher density of tobacco retailers, despite the fact that all the districts have approximately the same number of residents.


Substance Use & Suicide
- Substance use and suicide are also leading causes of death in San Francisco. Drug and alcohol use are especially important among adults 18 to 64 while suicide is one of the leading 5 causes of death for residents aged 13 to 34.


